---
-geometry: margin=2cm
-<!-- columns: 2 -->
-graphics: yes
-tables: yes
+geometry: a4paper, margin=2cm
+columns: 2
author: Andrew Lorimer
+header-includes:
+- \usepackage{fancyhdr}
+- \pagestyle{fancy}
+- \fancyhead[LO,LE]{Year 12 Methods}
+- \fancyhead[CO,CE]{Andrew Lorimer}
+- \usepackage{graphicx}
+- \usepackage{tabularx}
+- \usepackage[dvipsnames, table]{xcolor}
---
-
+\linespread{3}
\pagenumbering{gobble}
+\renewcommand{\arraystretch}{1.4}
+\definecolor{cas}{HTML}{e6f0fe}
-
-# Methods - Calculus
+# Calculus
## Average rate of change
$$m \operatorname{of} x \in [a,b] = {{f(b)-f(a)}\over {b - a}} = {dy \over dx}$$
-Average rate of change between $x=[a,b]$ given two points $P(a, f(a))$ and $Q(b, f(b))$ is the gradient $m$ of line $\overleftrightarrow{PQ}$
-
-On CAS: (Action|Interactive) -> Calculation -> Diff -> $f(x)$ or $y=\dots$
+\colorbox{cas}{On CAS:} Action $\rightarrow$ Calculation $\rightarrow$ `diff`
## Instantaneous rate of change
-Secant - line passing through two points on a curve
-Chord - line segment joining two points on a curve
-
-Estimated by using two given points on each side of the concerned point. Evaluate as in average rate of change.
-
-## Limits & continuity
+**Secant** - line passing through two points on a curve
+**Chord** - line segment joining two points on a curve
-### Limit theorems
+## Limit theorems
1. For constant function $f(x)=k$, $\lim_{x \rightarrow a} f(x) = k$
2. $\lim_{x \rightarrow a} (f(x) \pm g(x)) = F \pm G$
## Tangents & gradients
**Tangent line** - defined by $y=mx+c$ where $m={dy \over dx}$
-**Normal line** - $\perp$ tangent ($m_{\operatorname{tan}} \cdot m_{\operatorname{norm}} = -1$)
+**Normal line** - $\perp$ tangent ($m_{{tan}} \cdot m_{\operatorname{norm}} = -1$)
**Secant** $={{f(x+h)-f(x)} \over h}$
-$$\tan \Theta = m = f^\prime x$$
+\colorbox{cas}{On CAS:} Action $\rightarrow$ Calculation $\rightarrow$ Line $\rightarrow$ `tanLine` or `normal`
-where $\Theta$ is the angle that tangent line makes with +ve direction of $x$-axis
+## Strictly increasing/decreasing
-## Strictly increasing
+For $x_2$ and $x_1$ where $x_2 > x_1$:
-- Function $f$ is **strictly increasing** where $f(x_2) > f(x_1)$ and $x_2 > x_1$
-- Function $f$ is **strictly decreasing** where $f(x_2) < f(x_1)$ and $x_2 > x_1$
-- If $f^\prime (x) > 0$ for all $x$ in interval, then $f$ is **strictly increasing**
-- If $f^\prime(x) < 0$ for all $x$ in interval, then $f$ is **strictly decreasing**
+- **strictly increasing** where $f(x_2) > f(x_1)$
+or $f^\prime(x)>0$
+- **strictly decreasing** where $f(x_2) < f(x_1)$
+or $f^\prime(x)<0$
- Endpoints are included, even where gradient $=0$
+\columnbreak
+
### Solving on CAS
-**In main**: type function. Interactive -> Calculation -> Line -> (Normal | Tan line)
-**In graph**: define function. Analysis -> Sketch -> (Normal | Tan line). Type $x$ value to solve for a point. Return to show equation for line.
+\colorbox{cas}{\textbf{In main}}: type function. Interactive $\rightarrow$ Calculation $\rightarrow$ Line $\rightarrow$ (Normal | Tan line)
+\colorbox{cas}{\textbf{In graph}}: define function. Analysis $\rightarrow$ Sketch $\rightarrow$ (Normal | Tan line). Type $x$ value to solve for a point. Return to show equation for line.
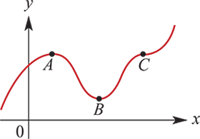
## Stationary points
Stationary where $m=0$.
Find derivative, solve for ${dy \over dx} = 0$
-{#id .class width=20%}
+\begin{center}
+ \includegraphics[height=3cm]{graphics/stationary-points.png}
+\end{center}
+
+**Local maximum at point $A$**
-**Local maximum at point $A$**
- $f^\prime (x) > 0$ left of $A$
- $f^\prime (x) < 0$ right of $A$
-**Local minimum at point $B$**
+**Local minimum at point $B$**
+
- $f^\prime (x) < 0$ left of $B$
- $f^\prime (x) > 0$ right of $B$
## Function derivatives
-
-| $f(x)$ | $f^\prime(x)$ |
-| ------ | ------------- |
-| $x^n$ | $nx^{n-1}$ |
-| $kx^n$ | $knx^{n-1}$ |
-| $g(x) + h(x)$ | $g^\prime (x) + h^\prime (x)$ |
-| $c$ | $0$ |
-| ${u \over v}$ | ${{v{du \over dx} - u{dv \over dx}} \over v^2}$ |
-| $uv$ | $u{dv \over dx} + v{du \over dx}$ |
-| $f \circ g$ | ${dy \over du} \cdot {du \over dx}$ |
-
+\definecolor{shade1}{HTML}{ffffff}
+\definecolor{shade2}{HTML}{F0F9E4}
+\rowcolors{1}{shade1}{shade2}
+\begin{tabularx}{\columnwidth}{rX}
+
+ \hline \(f(x)\) & \(f^\prime(x)\) \\ \hline
+
+ \hspace{6em} \(kx^n\) & \(knx^{n-1}\)\tabularnewline
+ \(g(x) \pm h(x)\) & \(g^\prime (x) \pm h^\prime (x)\)\tabularnewline
+ \(c\) & \(0\)\tabularnewline
+ \({u \over v}\) &
+ \({{(v{du \over dx} - u{dv \over dx}}) \div v^2}\)\tabularnewline
+ \(uv\) & \(u{dv \over dx} + v{du \over dx}\)\tabularnewline
+ \(f \circ g\) & \({dy \over du} \cdot {du \over dx}\)\tabularnewline
+ \(\sin ax\) & \(a\cos ax\)\tabularnewline
+ \(\sin(f(x))\) & \(f^\prime(x) \cdot \cos(f(x))\)\tabularnewline
+ \(\cos ax\) & \(-a \sin ax\)\tabularnewline
+ \(\cos(f(x))\) & \(f^\prime(x)(-\sin(f(x)))\) \\
+ \(e^{ax}\) & \(ae^{ax}\)\tabularnewline
+ \(\log_e {ax}\) & \(1 \over x\)\tabularnewline
+ \(\log_e f(x)\) & \(f^\prime (x) \over f(x)\)\tabularnewline
+
+ \hline
+
+\end{tabularx}